Difference between revisions of "CV Presentation Objects"
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background-color:#ffffff;"| [[File:CVArchitecturePresentationObjects.png|500px]] | | style="background-color:#ffffff;"| [[File:CVArchitecturePresentationObjects.png|500px]] | ||
| − | <div style='text-align: right;'>'''Notation'''</div> | + | <div style='text-align: right;'>'''[[Notation of Computational Viewpoint Models#Computational Objects|Notation]]'''</div> |
|} | |} | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:59, 4 April 2020
|
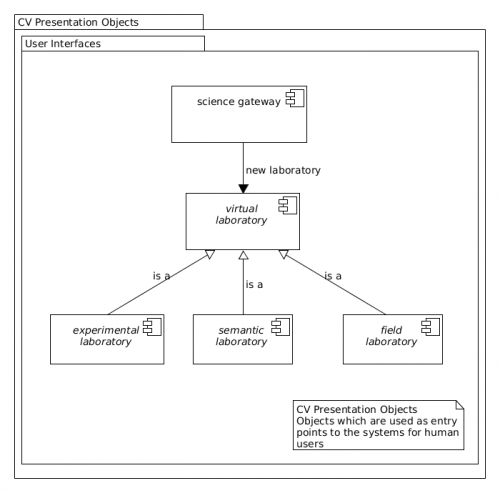
CV Presentation objects are the entry points for human users to the systems and services provided to access research data and their derived products. In the ENVRI RM, complex interactions between the components facilitating data use and other components are mediated by virtual laboratory; these objects are deployed by science gateways in order to provide a persistent context for such interactions between groups of users and components within the RI. The Reference Model recognises the following specific sub-classes of laboratory:
Regardless of provenance, all laboratories must interact with a AAAI service in order to authorise requests and authenticate users of the laboratory before they can proceed with any privileged activities. |
|
Contents
Science gateway[edit]

|
Community portal for interacting with an infrastructure.
A science gateway object encapsulates the functions required to interact with a research infrastructure from outside with the objects provided for data acquisition, data curation, data brokering and data processing. A science gateway should be able to provide virtual 'laboratories' for authorised agents to interact with and possibly configure many of the science functions of a research infrastructure. A science gateway is also known as a Virtual Research Environment.
- A science gateway object can instantiate any number of virtual laboratory objects.
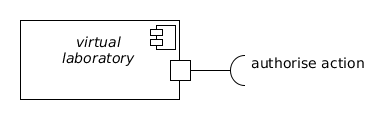
Virtual laboratory[edit]
|
Community proxy for interacting with RI components.
A virtual laboratory object encapsulates interaction between a user or group of users and a subset of the science functions provided by a research infrastructure. Its role is to bind a AAAI service with (potentially) any number of other infrastructure objects.
A virtual laboratory object must provide at least one interface:
- authorise action (client) is used to retrieve authorisation for any restricted interactions with the data acquisition components.
Specific sub-classes of virtual laboratory should be defined to interact with the infrastructure in different ways. The ENVRI RM defines the field laboratory object for interaction with the CV Data Acquisition components.
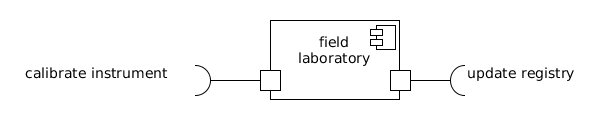
Field laboratory[edit]
|
Community proxy for interacting with data acquisition instruments.
A sub-class of virtual laboratory object encapsulating the functions required to access, calibrate, deploy or withhold instruments during the data acquisition phase.
Deployment of an instrument entails the deployment of an instrument controller by which the instrument can be interacted with.
- A field laboratory object can instantiate any number of instrument controller objects.
A field laboratory should provide at least two operational interfaces in addition to those provided by any virtual laboratory:
- calibrate instrument (client) is used to calibrate the reading of data by instruments based (in principle) on scientific analysis of data output. This interface can also be used to monitor activity on a given instrument.
- update registry (client) is used to register and/or withdraw instruments used for data acquisition.
A field laboratory is created by a science gateway in order to allow researchers in the field to interact with the data acquisition objects. The degree of freedom with which a field laboratory interacts with other data acquisition objects is contingent on the nature of the research infrastructure and policed by a AAAI service object (as defined for all user laboratories).
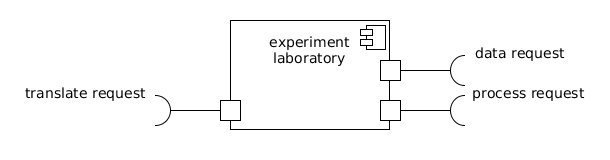
Experiment laboratory[edit]
|
Community proxy for conducting experiments within a research infrastructure.
A sub-class of virtual laboratory object encapsulating the functions required to schedule the processing of curated and user-provided data in order to perform some task (analysis, data mining, modelling, simulation, etc.).
An experiment laboratory should provide at least three operational interfaces:
- data request (client) is used to make requests of the research infrastructure pertaining to curated datasets.
- process request (client) is used to make requests of the research infrastructure pertaining to data processing.
- translate request (client) is used to invoke a semantic broker where some mapping between different semantic domains is deemed necessary.
An experiment laboratory is created by a science gateway to allow researchers interaction with data held by a research infrastructure in order to achieve some scientific output.
Semantic laboratory[edit]
|
Community proxy for interacting with semantic models.
A sub-class of virtual laboratory object encapsulating the functions required to update semantic models (such as ontologies) used in the interpretation of curated data (and infrastructure metadata).
A semantic laboratory should provide at least one operational interface in addition to those provided by any virtual laboratory:
- update model (client) is used to update semantic models associated with a research infrastructure.
- semantic data request (client) is used to make requests of the research infrastructure about metadata and annotations referring to data stored by the data set.
A semantic laboratory is created by a science gateway in order to allow researchers to provide input on the interpretation of data gathered by a research infrastructure.