Science Demonstrator 1: Support EISCAT 3D Users to Reprocess Data Using User's Algorithms (Use Case IC 3)
Please provide your feedback on this Science Demonstrator using the questionnaire at https://survey2.icos-cp.eu/ENVRIplus-evaluator!
Overview
Often the data products from a RI, derived from lower level/raw data, are pre-cooked. That means they are produced by applying some default processing algorithms and parameters, like spatial and temporal resolution, the use of model parameters, model and process selections. This demonstrator is an implementation results of IC_3 use case that describes a model that enables scientific researchers to re-process data by defining other selections of these inputs from other sources.
Scientific Objectives
EISCAT_3D is an environmental research infrastructure on the European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures (ESFRI) roadmap. Once assembled, it will be a world-leading international research infrastructure to study the high atmosphere in the Fenno-Scandinavian Arctic and to investigate how the Earth's atmosphere is coupled to space.
In general, EISCAT data products (including future EISCAT_3D data) are not raw data as sampled in the receivers, but have already undergone several steps of processing (along the chain voltages -> filtering -> time averaged spectral data -> inversion of physical parameters) by standard analysis algorithms in the EISCAT ICT system. This also implies that data are processed with a predefined set of parameters, e.g. spatial and temporal resolution, inversion model selection, model parameters and allowed parameter ranges.
This use case addressed a requirement of the EISCAT user community, namely to allow individual scientists to process the original experimental data using their own algorithms. The challenge in this use case is how to make use of ENVRIplus services to demonstrate that EISCAT scientists can re-process data by defining other selections of parameters and algorithms.
Description
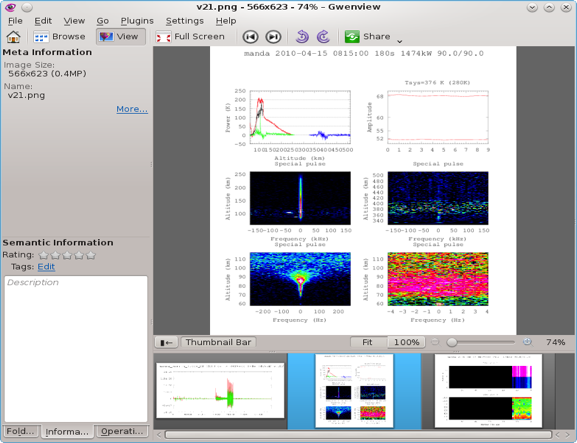
A typical usage scenario is that users select data together with an algorithm and invoke a workflow with tuned parameters. The data to be used in the test case is from the present EISCAT facilities, and the processing software is provided by EISCAT and originally written in Matlab. In this use case, we chose a Matlab processing package that could be converted into open source software. The process is to generate a graphical visualisation of the experimental data. Figure 1 shows the EISCAT Real Time Graph (RTG), which is primarily developed to follow the radar run in real-time and to produce a display of basic parameters, such as returned power spectra.